Why it's so hard for you to quit eating, even though you are not starving.
 There is also placing evidence connecting inequalities in the microbial varieties that compose the digestive tract microbiome to a number of health issue including allergic reactions, autoimmune problems, and psychiatric state of mind disorders.
There is also placing evidence connecting inequalities in the microbial varieties that compose the digestive tract microbiome to a number of health issue including allergic reactions, autoimmune problems, and psychiatric state of mind disorders.
Generally, these results suggest that modifications in intestinal tract inflammation can modify the trajectory of psychological state of mind disorders and that regulating the digestive tract microbiota may be a new method of treatment for patients experiencing these illness.
" This circuit appears to be the brain's method of telling you that if something preferences truly excellent, after that it's worth whatever cost you're paying to get to it, so do not quit," the leader of this research study said.
The presence of this animal mind circuit, explained in a paper in Nerve cell, may help clarify why humans so often overeat in our contemporary setting of bountiful and also tasty fare. The circuit is a byproduct of development, when large calorie-rich dishes were limited, therefore our brains were wired to feast on as numerous calories as humanly feasible since no person knew when the following very meal would come.
Various other research studies in computer mice have previously revealed that LGG can secure versus alcoholic liver condition and also non-alcoholic fatty liver illness. Saeedi claimed researches in human volunteers would certainly be needed to definitively evaluate the prospective clinical benefits of LGG in people.
After 5 weeks, the researchers assessed the rodents' microbiomes. They discovered that the germs had actually changed to establish brand-new characteristics.Under certain problems, the bacterium damaged the host, consuming the safety layer that lines the intestine. Previous research study has actually connected damage in this protective layer with irritable digestive tract disorder.
a brand-new research study from Baltimore's Sheppard Pratt Health and wellness System, performed by a study team led by Belief Dickerson, finds that a probiotic supplement might lower inflammation of the gut, which is known to exacerbate bipolar disorder. Probiotic microorganisms are non-pathogenic bacteria that, when present in the intestine plants, are understood to improve the general health and wellness of the host.
" This is the first time anyone anywhere has actually effectively engineered as well as printed an entire heart brimming with cells, capillary, ventricles as well as chambers," says Prof. Tal Dvir, who led the research for the study.
Researchers concentrated their research on the probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (known as LGG), a varieties common in several over-the-counter probiotic formulations. They offered mice food laced with LGG for two weeks and then analyzed just how they reacted to a high dose of acetaminophen.
n the situation of bipolar affective disorder and the GBA, previous research studies have actually shown that inflammation, or overstimulation of the body's immune system, is a contributing consider the disease. With this in mind, researchers established a probiotic supplement aimed at lowering swelling brought on by microbial inequalities in the digestive tract.
If you cherished this article and you would like to receive additional info relating to dbcngb kindly check out our internet site. For the research, a biopsy of fatty tissue was drawn from individuals. The cellular and a-cellular products of the cells were after that divided. While the cells were reprogrammed to become pluripotent stem cells, the extracellular matrix (ECM), a three-dimensional network of extracellular macromolecules such as collagen and glycoproteins, were processed right into a customized hydrogel that acted as the printing "ink.".
It has recognized that there is receptor Adora2a on endothelial cells, which generally supports healthy partnerships between mind task and also blood flow. The persistent activation of the receptor Adora2a can allow factors from the blood get in the brain and also impact the feature of our nerve cells. Troubles occur with chronic activation, specifically in the brain, which is what occurs with weight problems,.
Previous study by Saeedi's coworkers has mapped the molecular procedure through which LGG shows up to safeguard against oxidative liver injury. That study indicate the role of a protein called Nrf2, which regulates the expression of genes associated with dealing with cost-free radicals.
yet it can service nearly anything from nicknacks to living cells. In a major clinical innovation, Tel Aviv College scientists have "published" the world's initial 3D vascularised engineered heart making use of a patient's very own cells as well as organic materials. Their searchings for were published on April 15 in a research study in Advanced Science.
In the last few years, research study has demonstrated a solid web link in between the intestinal tract and the main nerves. This connection, named the "gut-brain axis" (GBA), permits crosstalk in between the endocrine, immune, and also free nerve systems. The GI system is additionally residence to the intestinal microbiome, a complicated populace of about 100 trillion bacteria (greater than ten times the number of cells that compose the body) that engages with the mucosal cellular lining of the GI system. Research studies have revealed that the intimate organization in between the digestive tract microbiome as well as GI tissue has a substantial result on the GBA.
How to protect skeletons of older women? Probiotics may work!
 It was first affirmed that probiotics supplements with health-promoting bacteria, can be used to affect the women skeleton. A related study from the University of Gothenburg, Sweden is under way to determine the role of probiotics in women bone loss. Women who received probiotics lose bone far more slowly, compared to women who received only a placebo. The research throws new light to prevent fractures among the elderly.
It was first affirmed that probiotics supplements with health-promoting bacteria, can be used to affect the women skeleton. A related study from the University of Gothenburg, Sweden is under way to determine the role of probiotics in women bone loss. Women who received probiotics lose bone far more slowly, compared to women who received only a placebo. The research throws new light to prevent fractures among the elderly.
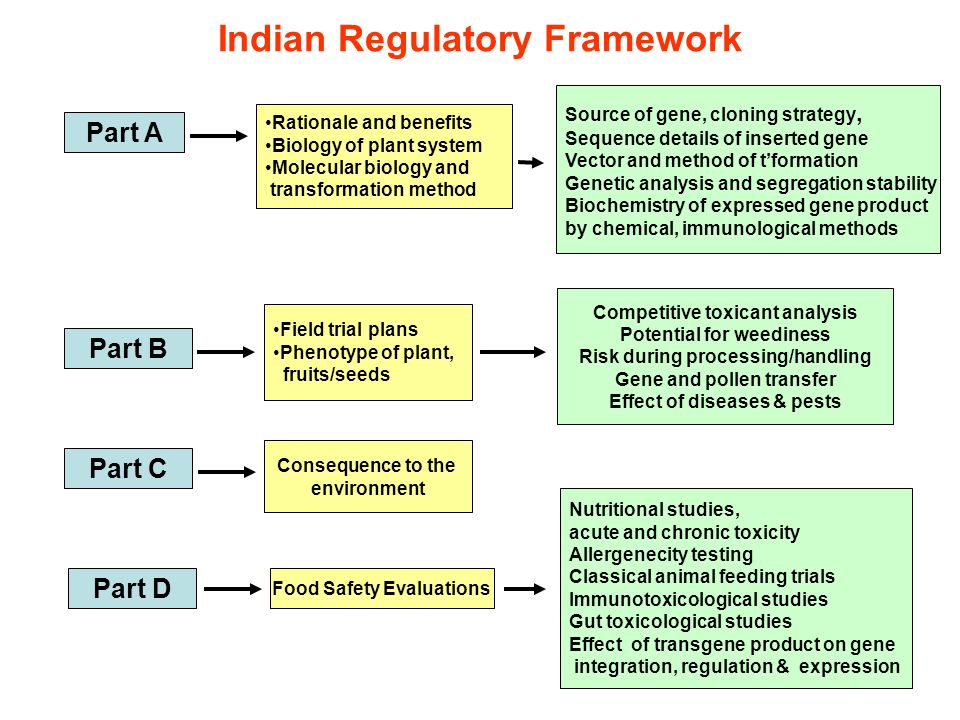
Background
Objective: Osteoporosis is characterized by a decrease in bone mass as well as a deterioration of the bone architecture resulting in an increased risk of fracture. Women, especially after menopause, are more vulnerable to bone loss than men. Osteoporosis is a commonly disease happened in elderly women(over 80 years of age)
"Today there are effective medications administered to treat osteoporosis, but because bone fragility is rarely detected before the first fracture, there is a pressing need for preventive treatments," says Mattias Lorentzon, who is a chief physician and professor of geriatrics at Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg.
This is the first time that researchers have shown that it is possible to cut age-related bone loss in elderly women in half if they receive health-promoting bacteria, known as probiotics.
Method
The study was conducted at Sahlgrenska University Hospital in Mölndal, Sweden, and its results of the study are now being published by the Journal of Internal Medicine. Ninety elderly women, 76 years old on average, ingested a powder that contained either health-promoting bacteria or a placebo every day for a whole year. A random method determined which women received the active treatment with the Lactobacillus reuteri 6475 bacteria and which received powder without bacteria. If you adored this article and you would like to collect more info with regards to Genomic Data (browse this site) nicely visit our site. Neither the researchers nor the women knew who received the active powder during the study.
Results
The discovery could have important implications in the future: "Older women are the group in society most at risk of osteoporosis and fractures. The fact that we have been able to show that treatment with probiotics can affect bone loss represents a paradigm shift. Treatment with probiotics can be an effective and safe way to prevent the onset of osteoporosis in many older people in the future," says Mattias Lorentzon.
Source: Science Daily
Original title: Probiotics can protect the skeletons of older women
Cell Reports: oral administraion of probiotics may reduce breast cancer's risk
"Lady Killer" --- breast cancer is the top cancer in women worldwide, the highest morbidity and mortality among female tumors (breast cancer, ovarian cancer, cervical cancer, endometrial cancer). Current preventive strategies for breast cancer include drug prophylaxis and preventive mastectomy, such as the famous star Angelina Jolie's double mastectomy, but not everyone can accept this way; and drug prophylaxis is limited to ER-positive breast cancer patients, who can be recommended to use endocrine therapies for prevention, there are no recommended drug prophylaxis for other patients. The latest study shows, in a paper published in Cell Reports, that diet especially affects the mammary gland microbiome, establishing an alternative mechanistic pathway for breast cancer prevention.
The latest study shows, in a paper published in Cell Reports, that diet especially affects the mammary gland microbiome, establishing an alternative mechanistic pathway for breast cancer prevention.
It was already known that malignant breast tumors have lower Lactobacillus abundance compared with benign lesions, implicating Lactobacillus as a negative regulator of breast cancer. Protective effects of Mediterranean diet pattern on breast cancer risk were also observed in a recent prospective cohort study. So scientists wanted to confirm that whether Mediterranean diet could increase mammary gland Lactobacillus abundance.
This study has chosen female monkeys (Macaca fascicularis) as research object, for the Macaca genus is closely related to humans, sharing a last common ancestor 25 million years ago. 40 female monkeys (M. fascicularis) were fed a Western diet or a Mediterranean diet for 31 months. The result shows that Consumption of Mediterranean diet was associated with 10-fold higher breast tissue Lactobacillus abundance, compared with a Western diet. It has been reported that oral consumption of Lactobacillus decreased triple-negative 4T1 breast cancer tumor growth in a syngeneic breast cancer model. If you beloved this article and also you would like to be given more info regarding DNA Database kindly visit our webpage. Above all, oral probiotics may establish an alternative mechanistic pathway for breast cancer prevention.
The researchers of this project will further study the physiological effects of increased lactic acid bacteria in breast cancer tissues. They will also evaluate oral probiotics interventions such as fish oil or probiotics supplements that affect microbial populations in breast and breast tumors.
The research about these is still ongoing, and we hope this research could be applied in clinical process in the foreseeable future.
Reference
Shively C A, Register T C, Appt S E, et al. Consumption of Mediterranean versus Western diet leads to distinct mammary gland microbiome populations[J]. Cell reports, 2018, 25(1): 47-56. e3.
Drama king: Your gut bacteria
 As for microbial 'drama king', it must say human gut bacteria which attracts your attention all the time! They're associated with nearly all aspects of your health. A series of frontier research results showed this:
As for microbial 'drama king', it must say human gut bacteria which attracts your attention all the time! They're associated with nearly all aspects of your health. A series of frontier research results showed this:
1. Charbonneau M , O'Donnell, David, Blanton L , et al. Sialylated Milk Oligosaccharides Promote Microbiota-Dependent Growth in Models of Infant Undernutrition[J]. Cell, 2016, 164(5):859-871.
2. Tang A T , Choi J P , Kotzin J J , et al. Endothelial TLR4 and the microbiome drive cerebral cavernous malformations[J]. Nature, 2017, 545(7654):305.
3. Liu B, Fang F, Pedersen N L, et al. Vagotomy and Parkinson disease[J]. Neurology, 2017, 88(21):1996-2002.
4. Rothhammer V , Borucki D M , Tjon E C , et al. Microglial control of astrocytes in response to microbial metabolites[J]. Nature, 2018.
5. Giada De Palma, Michael D. J. Lynch, Jun Lu, et al. Transplantation of fecal microbiota from patients with irritable bowel syndrome alters gut function and behavior in recipient mice, Science Translational Medicine 01 Mar 2017.
6. Ma C , Han M , Heinrich B , et al. Gut microbiome–mediated bile acid metabolism regulates liver cancer via NKT cells[J]. Science, 2018, 360(6391):eaan5931.
7. Atsushi Hayashi et al. Intestinal Dysbiosis and Biotin Deprivation Induce Alopecia through Overgrowth of Lactobacillus murinus in Mice, Cell Reports (2017).
The human gut microbiota refers to the all the microorganisms that inhabit the human gastrointestinal tract. Diverse roles of the gut microbiota in human health and disease have been recognized. Metagenomic studies have transformed our understanding of the taxonomic and functional diversity of human microbiota, but more than half of the sequencing reads from a typical human fecal metagenome cannot be mapped to existing bacterial reference genomes3,4 . The lack of high-quality reference genomes has become an obstacle for high-resolution analyses of the human gut microbiome.
A new study shows, in a paper published in Nature biotechnology, that the Culturable Genome Reference (CGR), a collection of 1,520 nonredundant, high-quality draft genomes generated from >6,000 bacteria cultivated from fecal samples of healthy humans. Of the 1,520 genomes, which were chosen to cover all major bacterial phyla and genera in the human gut, 264 are not represented in existing reference genome catalogs.
The CGR will improve metagenomic analyses, genome variation analyses, functional characterization and pan-genome analyses. The isolated gut bacteria strains have been deposited in the China National GeneBank (CNGB), the accession ID is CNP0000126. which may be useful for studies that aim to alter microbiota functions, as novel probiotics, or for verification of disease-associated bacterial markers.
Reference: Zou Y, Xue W, Luo G, et al. 1,520 reference genomes from cultivated human gut bacteria enable functional microbiome analyses[J]. Nature biotechnology, 2019, 37(2): 179.
Probiotics, a potential new avenue for treatment of bipolar disorder
Probioticscould help millions of patients suffering from bipolar disorder.
What's bipolar disorder
About 3 million people in the US are diagnosed every year with bipolar disorder, a psychiatric condition characterized by dramatic shifts in mood from depression to mania. Currently, the standard treatment includes a combination of psychotherapy and prescription medications such as mood stabilizers and antipsychotics.
a new study from Baltimore's Sheppard Pratt Health System, conducted by a research team led by Faith Dickerson, finds that a probiotic supplement may reduce inflammation of the gut, which is known to exacerbate bipolar disorder. Probiotic organisms are non-pathogenic bacteria that, when present in the gut flora, are known to improve the overall health of the host.
Background
In recent years, research has demonstrated a strong link between the gastrointestinal tract and the central nervous system. This connection, named the "gut-brain axis" (GBA), allows for crosstalk between the endocrine, immune, and autonomic nervous systems. The GI tract is also home to the intestinal microbiome, a complex population of roughly 100 trillion microorganisms (more than ten times the number of cells that make up the human body) that interacts with the mucosal lining of the GI tract. Studies have shown that the intimate association between the gut microbiome and GI tissue has a significant effect on the GBA.
There is also mounting evidence linking imbalances in the microbial species that make up the gut microbiome to a number of health problems including allergies, autoimmune disorders, and psychiatric mood disorders.
Method
n the case of bipolar disorder and the GBA, previous studies have shown that inflammation, or overstimulation of the body's immune system, is a contributing factor in the disease. With this in mind, researchers developed a probiotic supplement aimed at reducing inflammation caused by microbial imbalances in the gut.
A group of patients recently hospitalized for mania participated in a 6-month study to track the effects of probiotic treatment on both their mood and the status of their immune system.
The patients were randomly selected to receive either the probiotic supplement or a placebo in addition to their usual medications. The results showed that the group receiving the probiotic supplement, on average, didn't return to the hospital as quickly and required less in-patient treatment time compared to the placebo group. If you have any questions regarding where and ways to use dbcngb, you can call us at the page. The beneficial effects were most pronounced in those patients who exhibited abnormally high levels of inflammation at the beginning of the study.
Results
Overall, these results indicate that changes in intestinal inflammation can alter the trajectory of psychiatric mood disorders and that modulating the intestinal microbiota may be a new avenue of treatment for patients suffering from these diseases.
Source:Science Daily
Original title:Probiotics could help millions of patients suffering from bipolar disorder
Children get diarrhea, asthma, and overweight!Because of gut microbiota
 What is gut microbiota?
What is gut microbiota?
The human intestinal microbiota is the collective name of all microorganisms that live in our gut. The developing infant gut microbiota (IGM) is highly dynamic and prone to disruption by external factors.
If you loved this write-up and you would like to get additional data with regards to cngb kindly stop by our own web-site. The source of infant gut microbiota:
Early colonization of the infant gastrointestinal tract is crucial for the overall health of the infant. Microbes colonize the neonatal gut immediately following birth, and establishment and maintenance of non-pathogenic intestinal microbiota may reduce several neonatal inflammatory conditions. Much effort has therefore been devoted to manipulation of the composition of the microbiota:
1) For infants of natural childbirth, the initial colonizations are mainly from their mother 's stool, vagina or skin
2) For infants of caesarean, the initial colonizations are derived from the surrounding environment such as the surgical environment, medical equipment or the hands of the nursing staff
3) The role of early infant nutrition, particularly breast milk, and supplementation of infant formula with prebiotics that positively influence the enteric microbiota by selectively promoting growth of beneficial bacteria
4) Oral administration of probiotic bacteria which when administered in adequate amounts confer a health benefit on the host
A new research shows that breastfeeding duration in early life and pre-school dietary lifestyle correlated with the composition and functional competences of the gut microbiota in the children at school age. Metagenomic sequencing data for all 281 children samples in this study have been deposited in the China Nucleotide Sequence Archive (CNSA): CNP0000037.
Children get diarrhea, asthma, and overweight!Because of gut microbiota
Children get diarrhea, asthma, and overweight!Because of gut microbiota. As a lot of research shows that intestinal bacteria also play a role in children diarrhea, asthma, and overweight.
The Gut Microbiome's Role in diarrhea
Diarrhea is when stools (bowel movements) are loose and watery. Diarrhea is a common problem. It may last 1 or 2 days and go away on its own.
The Gut Microbiome's Role in asthma
Susan Lynch and Kei E. Fujimura of the University of California San Francisco present the latest research in mice exploring this relationship, especially how specific types of bacteria alter the presence of different immune cells. Though still an emerging body of work, they believe it is evidence that manipulation of the airway/gut microbiome at an early age could lead to new strategies to prevent or manage asthma.
The Gut Microbiome's Role in obesity
"Our study provides more evidence that the gut microbiota might be playing a role in later obesity," said lead author Maggie Stanislawski, PhD, who is a research associate at the LEAD Center, University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Colorado School of Public Health, Aurora, Colorado. "If our findings can be confirmed by other studies, the gut microbiota might play an important part of the obesity prediction algorithm, to identify at-risk kids early in life, before they start to gain any excess weight that might put them at risk for later obesity."
Even more, some research showed that microbial composition of the human gut at 1 year of age predicts cognitive performance at 2 years of age, particularly in the area of communicative behavior.
The following is result from one of the latest research, metagenomic sequencing data for all 281 children samples in this study have been deposited in the China Nucleotide Sequence Archive (CNSA): CNP0000037.
Please keep on paying attention to CNGBdb.
Source:Science Daily
Original headlines:
1. The infant gut microbiome: New studies on its origins and how it's knocked out of balance
2. Gut microbiota of infants predicts obesity in children